Polymer Project Logo on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A polymer (; Greek '' poly-'', "many" + '' -mer'', "part")
is a substance or
A polymer (; Greek '' poly-'', "many" + '' -mer'', "part")
is a substance or
 A polymer (; Greek '' poly-'', "many" + '' -mer'', "part")
is a substance or
A polymer (; Greek '' poly-'', "many" + '' -mer'', "part")
is a substance or material
Material is a substance or mixture of substances that constitutes an object. Materials can be pure or impure, living or non-living matter. Materials can be classified on the basis of their physical and chemical properties, or on their geologi ...
consisting of very large molecule
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms held together by attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions which satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemistry, and bioch ...
s called macromolecule
A macromolecule is a very large molecule important to biophysical processes, such as a protein or nucleic acid. It is composed of thousands of covalently bonded atoms. Many macromolecules are polymers of smaller molecules called monomers. The ...
s, composed of many repeating subunits. Due to their broad spectrum of properties, both synthetic and natural polymers play essential and ubiquitous roles in everyday life. Polymers range from familiar synthetic plastics such as polystyrene
Polystyrene (PS) is a synthetic polymer made from monomers of the aromatic hydrocarbon styrene. Polystyrene can be solid or foamed. General-purpose polystyrene is clear, hard, and brittle. It is an inexpensive resin per unit weight. It is a ...
to natural biopolymer
Biopolymers are natural polymers produced by the cells of living organisms. Like other polymers, biopolymers consist of monomeric units that are covalently bonded in chains to form larger molecules. There are three main classes of biopolymers, cl ...
s such as DNA and protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, respo ...
s that are fundamental to biological structure and function. Polymers, both natural and synthetic, are created via polymerization
In polymer chemistry, polymerization (American English), or polymerisation (British English), is a process of reacting monomer, monomer molecules together in a chemical reaction to form polymer chains or three-dimensional networks. There are ...
of many small molecules, known as monomer
In chemistry, a monomer ( ; ''mono-'', "one" + '' -mer'', "part") is a molecule that can react together with other monomer molecules to form a larger polymer chain or three-dimensional network in a process called polymerization.
Classification
Mo ...
s. Their consequently large molecular mass
The molecular mass (''m'') is the mass of a given molecule: it is measured in daltons (Da or u). Different molecules of the same compound may have different molecular masses because they contain different isotopes of an element. The related quanti ...
, relative to small molecule
Within the fields of molecular biology and pharmacology, a small molecule or micromolecule is a low molecular weight (≤ 1000 daltons) organic compound that may regulate a biological process, with a size on the order of 1 nm. Many drugs ar ...
compound
Compound may refer to:
Architecture and built environments
* Compound (enclosure), a cluster of buildings having a shared purpose, usually inside a fence or wall
** Compound (fortification), a version of the above fortified with defensive struct ...
s, produces unique physical properties
A physical property is any property that is measurable, whose value describes a state of a physical system. The changes in the physical properties of a system can be used to describe its changes between momentary states. Physical properties are o ...
including toughness
In materials science and metallurgy, toughness is the ability of a material to absorb energy and plastically deform without fracturing.elasticity, 
 Polymers are of two types: naturally occurring and synthetic or ''man made''.
Polymers are of two types: naturally occurring and synthetic or ''man made''.
 Polymerization is the process of combining many
Polymerization is the process of combining many  Newer methods, such as
Newer methods, such as
 There are three main classes of biopolymers:
There are three main classes of biopolymers:
 An important microstructural feature of a polymer is its architecture and shape, which relates to the way branch points lead to a deviation from a simple linear chain. A branched polymer molecule is composed of a main chain with one or more substituent side chains or branches. Types of branched polymers include star polymers,
An important microstructural feature of a polymer is its architecture and shape, which relates to the way branch points lead to a deviation from a simple linear chain. A branched polymer molecule is composed of a main chain with one or more substituent side chains or branches. Types of branched polymers include star polymers,
 The bulk properties of a polymer are those most often of end-use interest. These are the properties that dictate how the polymer actually behaves on a macroscopic scale.
The bulk properties of a polymer are those most often of end-use interest. These are the properties that dictate how the polymer actually behaves on a macroscopic scale.
 In general, polymeric mixtures are far less miscible than mixtures of
In general, polymeric mixtures are far less miscible than mixtures of
How to Analyze Polymers Using X-ray DiffractionPolymer Chemistry Hypertext, Educational resourceIntroduction to Polymers
{{Portal bar, Science, Chemistry, Numismatics, Electronics, Algae, Money Organic polymers, Polymers, Polymer chemistry Soft matter Materials science
viscoelasticity
In materials science and continuum mechanics, viscoelasticity is the property of materials that exhibit both viscous and elastic characteristics when undergoing deformation. Viscous materials, like water, resist shear flow and strain linearly wi ...
, and a tendency to form amorphous
In condensed matter physics and materials science, an amorphous solid (or non-crystalline solid, glassy solid) is a solid that lacks the long-range order that is characteristic of a crystal.
Etymology
The term comes from the Greek ''a'' ("wi ...
and semicrystalline
Crystallinity refers to the degree of structural order in a solid. In a crystal, the atoms or molecules are arranged in a regular, periodic manner. The degree of crystallinity has a big influence on hardness, density, transparency and diffusion ...
structures rather than crystal
A crystal or crystalline solid is a solid material whose constituents (such as atoms, molecules, or ions) are arranged in a highly ordered microscopic structure, forming a crystal lattice that extends in all directions. In addition, macros ...
s.
The term "polymer" derives from the Greek word πολύς (''polus'', meaning "many, much") and μέρος (''meros'', meaning "part"). The term was coined in 1833 by Jöns Jacob Berzelius
Baron Jöns Jacob Berzelius (; by himself and his contemporaries named only Jacob Berzelius, 20 August 1779 – 7 August 1848) was a Swedish chemist. Berzelius is considered, along with Robert Boyle, John Dalton, and Antoine Lavoisier, to be on ...
, though with a definition distinct from the modern IUPAC
The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC ) is an international federation of National Adhering Organizations working for the advancement of the chemical sciences, especially by developing nomenclature and terminology. It is ...
definition. The modern concept of polymers as covalently bonded macromolecular structures was proposed in 1920 by Hermann Staudinger
Hermann Staudinger (; 23 March 1881 – 8 September 1965) was a German organic chemist who demonstrated the existence of macromolecules, which he characterized as polymers. For this work he received the 1953 Nobel Prize in Chemistry.
He is also ...
, who spent the next decade finding experimental evidence for this hypothesis.
Polymers are studied in the fields of polymer science
Polymer science or macromolecular science is a subfield of materials science concerned with polymers, primarily synthetic polymers such as plastics and elastomers. The field of polymer science includes researchers in multiple disciplines includ ...
(which includes polymer chemistry
Polymer chemistry is a sub-discipline of chemistry that focuses on the structures of chemicals, chemical synthesis, and chemical and physical properties of polymers and macromolecules. The principles and methods used within polymer chemistry are ...
and polymer physics), biophysics
Biophysics is an interdisciplinary science that applies approaches and methods traditionally used in physics to study biological phenomena. Biophysics covers all scales of biological organization, from molecular to organismic and populations. ...
and materials science and engineering. Historically, products arising from the linkage of repeating units by covalent
A covalent bond is a chemical bond that involves the sharing of electrons to form electron pairs between atoms. These electron pairs are known as shared pairs or bonding pairs. The stable balance of attractive and repulsive forces between atoms ...
chemical bond
A chemical bond is a lasting attraction between atoms or ions that enables the formation of molecules and crystals. The bond may result from the electrostatic force between oppositely charged ions as in ionic bonds, or through the sharing of ...
s have been the primary focus of polymer science. An emerging important area now focuses on supramolecular polymers formed by non-covalent links. Polyisoprene
Polyisoprene is strictly speaking a collective name for Polymer, polymers that are produced by polymerization of isoprene. In practice polyisoprene is commonly used to refer to synthetic ''cis''-1,4-polyisoprene, made by the industrial polymerisa ...
of latex
Latex is an emulsion (stable dispersion) of polymer microparticles in water. Latexes are found in nature, but synthetic latexes are common as well.
In nature, latex is found as a milky fluid found in 10% of all flowering plants (angiosperms ...
rubber
Rubber, also called India rubber, latex, Amazonian rubber, ''caucho'', or ''caoutchouc'', as initially produced, consists of polymers of the organic compound isoprene, with minor impurities of other organic compounds. Thailand, Malaysia, and ...
is an example of a natural polymer, and the polystyrene
Polystyrene (PS) is a synthetic polymer made from monomers of the aromatic hydrocarbon styrene. Polystyrene can be solid or foamed. General-purpose polystyrene is clear, hard, and brittle. It is an inexpensive resin per unit weight. It is a ...
of styrofoam
Styrofoam is a trademarked brand of closed-cell extruded polystyrene foam (XPS), commonly called "Blue Board", manufactured as foam continuous building insulation board used in walls, roofs, and foundations as thermal insulation and water barrie ...
is an example of a synthetic polymer. In biological contexts, essentially all biological macromolecule
A macromolecule is a very large molecule important to biophysical processes, such as a protein or nucleic acid. It is composed of thousands of covalently bonded atoms. Many macromolecules are polymers of smaller molecules called monomers. The ...
s—i.e., proteins (polyamides), nucleic acid
Nucleic acids are biopolymers, macromolecules, essential to all known forms of life. They are composed of nucleotides, which are the monomers made of three components: a 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base. The two main cl ...
s (polynucleotides), and polysaccharides—are purely polymeric, or are composed in large part of polymeric components.

Common examples
 Polymers are of two types: naturally occurring and synthetic or ''man made''.
Polymers are of two types: naturally occurring and synthetic or ''man made''.
Natural
Natural polymeric materials such ashemp
Hemp, or industrial hemp, is a botanical class of ''Cannabis sativa'' cultivars grown specifically for industrial or medicinal use. It can be used to make a wide range of products. Along with bamboo, hemp is among the fastest growing plants o ...
, shellac
Shellac () is a resin secreted by the female lac bug on trees in the forests of India and Thailand. It is processed and sold as dry flakes and dissolved in alcohol to make liquid shellac, which is used as a brush-on colorant, food glaze and ...
, amber
Amber is fossilized tree resin that has been appreciated for its color and natural beauty since Neolithic times. Much valued from antiquity to the present as a gemstone, amber is made into a variety of decorative objects."Amber" (2004). In Ma ...
, wool
Wool is the textile fibre obtained from sheep and other mammals, especially goats, rabbits, and camelids. The term may also refer to inorganic materials, such as mineral wool and glass wool, that have properties similar to animal wool.
As ...
, silk
Silk is a natural protein fiber, some forms of which can be woven into textiles. The protein fiber of silk is composed mainly of fibroin and is produced by certain insect larvae to form cocoons. The best-known silk is obtained from the coc ...
, and natural rubber
Rubber, also called India rubber, latex, Amazonian rubber, ''caucho'', or ''caoutchouc'', as initially produced, consists of polymers of the organic compound isoprene, with minor impurities of other organic compounds. Thailand, Malaysia, and ...
have been used for centuries. A variety of other natural polymers exist, such as cellulose
Cellulose is an organic compound with the formula , a polysaccharide consisting of a linear chain of several hundred to many thousands of β(1→4) linked D-glucose units. Cellulose is an important structural component of the primary cell wall ...
, which is the main constituent of wood and paper.
Synthetic
Thelist of synthetic polymers
Some familiar household synthetic polymers include: Nylons in textiles and fabrics, Teflon in non-stick pans, Bakelite for electrical switches, polyvinyl chloride (PVC) in pipes, etc. The common PET bottles are made of a synthetic polymer, polye ...
, roughly in order of worldwide demand, includes polyethylene
Polyethylene or polythene (abbreviated PE; IUPAC name polyethene or poly(methylene)) is the most commonly produced plastic. It is a polymer, primarily used for packaging ( plastic bags, plastic films, geomembranes and containers including bo ...
, polypropylene
Polypropylene (PP), also known as polypropene, is a thermoplastic polymer used in a wide variety of applications. It is produced via chain-growth polymerization from the monomer propylene.
Polypropylene
belongs to the group of polyolefins and ...
, polystyrene
Polystyrene (PS) is a synthetic polymer made from monomers of the aromatic hydrocarbon styrene. Polystyrene can be solid or foamed. General-purpose polystyrene is clear, hard, and brittle. It is an inexpensive resin per unit weight. It is a ...
, polyvinyl chloride, synthetic rubber
A synthetic rubber is an artificial elastomer. They are polymers synthesized from petroleum byproducts. About 32-million metric tons of rubbers are produced annually in the United States, and of that amount two thirds are synthetic. Synthetic rubbe ...
, phenol formaldehyde resin
Phenol formaldehyde resins (PF) or phenolic resins (also infrequently called phenoplasts) are synthetic polymers obtained by the reaction of phenol or substituted phenol with formaldehyde. Used as the basis for Bakelite, PFs were the first commerc ...
(or Bakelite
Polyoxybenzylmethylenglycolanhydride, better known as Bakelite ( ), is a thermosetting phenol formaldehyde resin, formed from a condensation reaction of phenol with formaldehyde. The first plastic made from synthetic components, it was developed ...
), neoprene
Neoprene (also polychloroprene) is a family of synthetic rubbers that are produced by polymerization of chloroprene.Werner Obrecht, Jean-Pierre Lambert, Michael Happ, Christiane Oppenheimer-Stix, John Dunn and Ralf Krüger "Rubber, 4. Emulsion R ...
, nylon
Nylon is a generic designation for a family of synthetic polymers composed of polyamides ( repeating units linked by amide links).The polyamides may be aliphatic or semi-aromatic.
Nylon is a silk-like thermoplastic, generally made from petro ...
, polyacrylonitrile
Polyacrylonitrile (PAN), also known as polyvinyl cyanide and Creslan 61, is a synthetic, semicrystalline organic polymer resin, with the linear formula (C3H3N)n. Though it is thermoplastic, it does not melt under normal conditions. It degrades bef ...
, PVB, silicone
A silicone or polysiloxane is a polymer made up of siloxane (−R2Si−O−SiR2−, where R = organic group). They are typically colorless oils or rubber-like substances. Silicones are used in sealants, adhesives, lubricants, medicine, cooking ...
, and many more. More than 330 million tons of these polymers are made every year (2015).
Most commonly, the continuously linked backbone of a polymer used for the preparation of plastics consists mainly of carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element with the symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalent
In chemistry, the valence (US spelling) or valency (British spelling) of an element is the measure of its combining capacity with o ...
atoms. A simple example is polyethylene ('polythene' in British English), whose repeat unit or monomer is ethylene
Ethylene (IUPAC name: ethene) is a hydrocarbon which has the formula or . It is a colourless, flammable gas with a faint "sweet and musky" odour when pure. It is the simplest alkene (a hydrocarbon with carbon-carbon double bonds).
Ethylene i ...
. Many other structures do exist; for example, elements such as silicon form familiar materials such as silicones, examples being Silly Putty
Silly Putty is a toy based on silicone polymers that have unusual physical properties. It bounces, but it breaks when given a sharp blow, and it can also flow like a liquid. It contains a viscoelastic liquid silicone, a type of non-Newtonian f ...
and waterproof plumbing sealant. Oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as wel ...
is also commonly present in polymer backbones, such as those of polyethylene glycol
Polyethylene glycol (PEG; ) is a polyether compound derived from petroleum with many applications, from industrial manufacturing to medicine. PEG is also known as polyethylene oxide (PEO) or polyoxyethylene (POE), depending on its molecular we ...
, polysaccharide
Polysaccharides (), or polycarbohydrates, are the most abundant carbohydrates found in food. They are long chain polymeric carbohydrates composed of monosaccharide units bound together by glycosidic linkages. This carbohydrate can react with wa ...
s (in glycosidic bond
A glycosidic bond or glycosidic linkage is a type of covalent bond that joins a carbohydrate (sugar) molecule to another group, which may or may not be another carbohydrate.
A glycosidic bond is formed between the hemiacetal or hemiketal group ...
s), and DNA (in phosphodiester bond
In chemistry, a phosphodiester bond occurs when exactly two of the hydroxyl groups () in phosphoric acid react with hydroxyl groups on other molecules to form two ester bonds. The "bond" involves this linkage . Discussion of phosphodiesters is ...
s).
History
Polymers have been essential components of commodities since the early days of humankind. The use ofwool
Wool is the textile fibre obtained from sheep and other mammals, especially goats, rabbits, and camelids. The term may also refer to inorganic materials, such as mineral wool and glass wool, that have properties similar to animal wool.
As ...
(keratin
Keratin () is one of a family of structural fibrous proteins also known as ''scleroproteins''. Alpha-keratin (α-keratin) is a type of keratin found in vertebrates. It is the key structural material making up scales, hair, nails, feathers, ho ...
), cotton
Cotton is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll, or protective case, around the seeds of the cotton plants of the genus ''Gossypium'' in the mallow family Malvaceae. The fiber is almost pure cellulose, and can contain minor perce ...
and linen
Linen () is a textile made from the fibers of the flax plant.
Linen is very strong, absorbent, and dries faster than cotton. Because of these properties, linen is comfortable to wear in hot weather and is valued for use in garments. It also ...
fibres (cellulose
Cellulose is an organic compound with the formula , a polysaccharide consisting of a linear chain of several hundred to many thousands of β(1→4) linked D-glucose units. Cellulose is an important structural component of the primary cell wall ...
) for garments, paper reed (cellulose
Cellulose is an organic compound with the formula , a polysaccharide consisting of a linear chain of several hundred to many thousands of β(1→4) linked D-glucose units. Cellulose is an important structural component of the primary cell wall ...
) for paper
Paper is a thin sheet material produced by mechanically or chemically processing cellulose fibres derived from wood, rags, grasses or other vegetable sources in water, draining the water through fine mesh leaving the fibre evenly distributed ...
are just a few examples of how our ancestors exploited polymer-containing raw materials to obtain artefacts. The latex sap of “caoutchouc” trees (natural rubber
Rubber, also called India rubber, latex, Amazonian rubber, ''caucho'', or ''caoutchouc'', as initially produced, consists of polymers of the organic compound isoprene, with minor impurities of other organic compounds. Thailand, Malaysia, and ...
) reached Europe in the 16th century from South America long after the Olmec
The Olmecs () were the earliest known major Mesoamerican civilization. Following a progressive development in Soconusco, they occupied the tropical lowlands of the modern-day Mexican states of Veracruz and Tabasco. It has been speculated that t ...
, Maya
Maya may refer to:
Civilizations
* Maya peoples, of southern Mexico and northern Central America
** Maya civilization, the historical civilization of the Maya peoples
** Maya language, the languages of the Maya peoples
* Maya (Ethiopia), a populat ...
and Aztec
The Aztecs () were a Mesoamerican culture that flourished in central Mexico in the post-classic period from 1300 to 1521. The Aztec people included different Indigenous peoples of Mexico, ethnic groups of central Mexico, particularly those g ...
had started using it as a material to make balls, waterproof textiles and containers.
The chemical manipulation of polymers dates back to the 19th century, although at the time the nature of these species was not understood. The behaviour of polymers was initially rationalised according to the theory proposed by Thomas Graham which considered them as colloidal aggregates of small molecules held together by unknown forces.
Notwithstanding the lack of theoretical knowledge, the potential of polymers to provide innovative, accessible and cheap materials was immediately grasped. The work carried out by Braconnot, Parkes Parkes may refer to:
* Sir Henry Parkes (1815–1896), Australian politician, one of the earliest and most prominent advocates for Australian federation
Named for Henry Parkes
* Parkes, New South Wales, a regional town
* Parkes Observatory, a radi ...
, Ludersdorf, Hayard and many others on the modification of natural polymers determined many significant advances in the field. Their contributions led to the discovery of materials such as celluloid
Celluloids are a class of materials produced by mixing nitrocellulose and camphor, often with added dyes and other agents. Once much more common for its use as photographic film before the advent of safer methods, celluloid's common contemporar ...
, galalith
Galalith (Erinoid in the United Kingdom) is a synthetic plastic material manufactured by the interaction of casein and formaldehyde. The commercial name is derived from the Ancient Greek words (, "milk") and (, "stone"). It is odourless, insol ...
, parkesine
Celluloids are a class of materials produced by mixing nitrocellulose and camphor, often with added dyes and other agents. Once much more common for its use as photographic film before the advent of safer methods, celluloid's common contemporar ...
, rayon
Rayon is a semi-synthetic fiber, made from natural sources of regenerated cellulose, such as wood and related agricultural products. It has the same molecular structure as cellulose. It is also called viscose. Many types and grades of viscose f ...
, vulcanised rubber and, later, Bakelite
Polyoxybenzylmethylenglycolanhydride, better known as Bakelite ( ), is a thermosetting phenol formaldehyde resin, formed from a condensation reaction of phenol with formaldehyde. The first plastic made from synthetic components, it was developed ...
: all materials that quickly entered industrial manufacturing processes and reached households as garments components (''e.g.'', fabrics, buttons), crockery and decorative items.
In 1920, Hermann Staudinger
Hermann Staudinger (; 23 March 1881 – 8 September 1965) was a German organic chemist who demonstrated the existence of macromolecules, which he characterized as polymers. For this work he received the 1953 Nobel Prize in Chemistry.
He is also ...
published his seminal work “Über Polymerisation”, in which he proposed that polymers were in fact long chains of atoms linked by covalent bonds. His work was debated at length, but eventually it was accepted by the scientific community. Because of this work, Staudinger was awarded the Nobel Prize in 1953.
After the 1930s polymers entered a golden age during which new types were discovered and quickly given commercial applications, replacing naturally-sourced materials. This development was fuelled by an industrial sector with a strong economic drive and it was supported by a broad academic community that contributed innovative syntheses of monomers from cheaper raw material, more efficient polymerisation processes, improved techniques for polymer characterisation and advanced, theoretical understanding of polymers.
Since 1953, six Nobel prizes have been awarded in the area of polymer science, excluding those for research on biological macromolecules. This further testifies to its impact on modern science and technology. As Lord Todd
Alexander Robertus Todd, Baron Todd (2 October 1907 – 10 January 1997) was a British biochemist whose research on the structure and synthesis of nucleotides, nucleosides, and nucleotide coenzymes gained him the Nobel Prize for Chemistry in 1 ...
summarised in 1980, “I am inclined to think that the development of polymerization is perhaps the biggest thing that chemistry has done, where it has had the biggest effect on everyday life”.
Synthesis
 Polymerization is the process of combining many
Polymerization is the process of combining many small molecule
Within the fields of molecular biology and pharmacology, a small molecule or micromolecule is a low molecular weight (≤ 1000 daltons) organic compound that may regulate a biological process, with a size on the order of 1 nm. Many drugs ar ...
s known as monomers into a covalently bonded chain or network. During the polymerization process, some chemical groups may be lost from each monomer. This happens in the polymerization of PET polyester. The monomers are terephthalic acid (HOOCC6H4COOH) and ethylene glycol
Ethylene glycol (IUPAC name: ethane-1,2-diol) is an organic compound (a vicinal diol) with the formula . It is mainly used for two purposes, as a raw material in the manufacture of polyester fibers and for antifreeze formulations. It is an odo ...
(HOCH2CH2OH) but the repeating unit is OCC6H4COOCH2CH2O, which corresponds to the combination of the two monomers with the loss of two water molecules. The distinct piece of each monomer that is incorporated into the polymer is known as a repeat unit
In polymer chemistry, a repeat unit or repeating unit (or mer) is a part of a polymer whose repetition would produce the complete polymer chain (except for the end-groups) by linking the repeat units together successively along the chain, like the ...
or monomer residue.
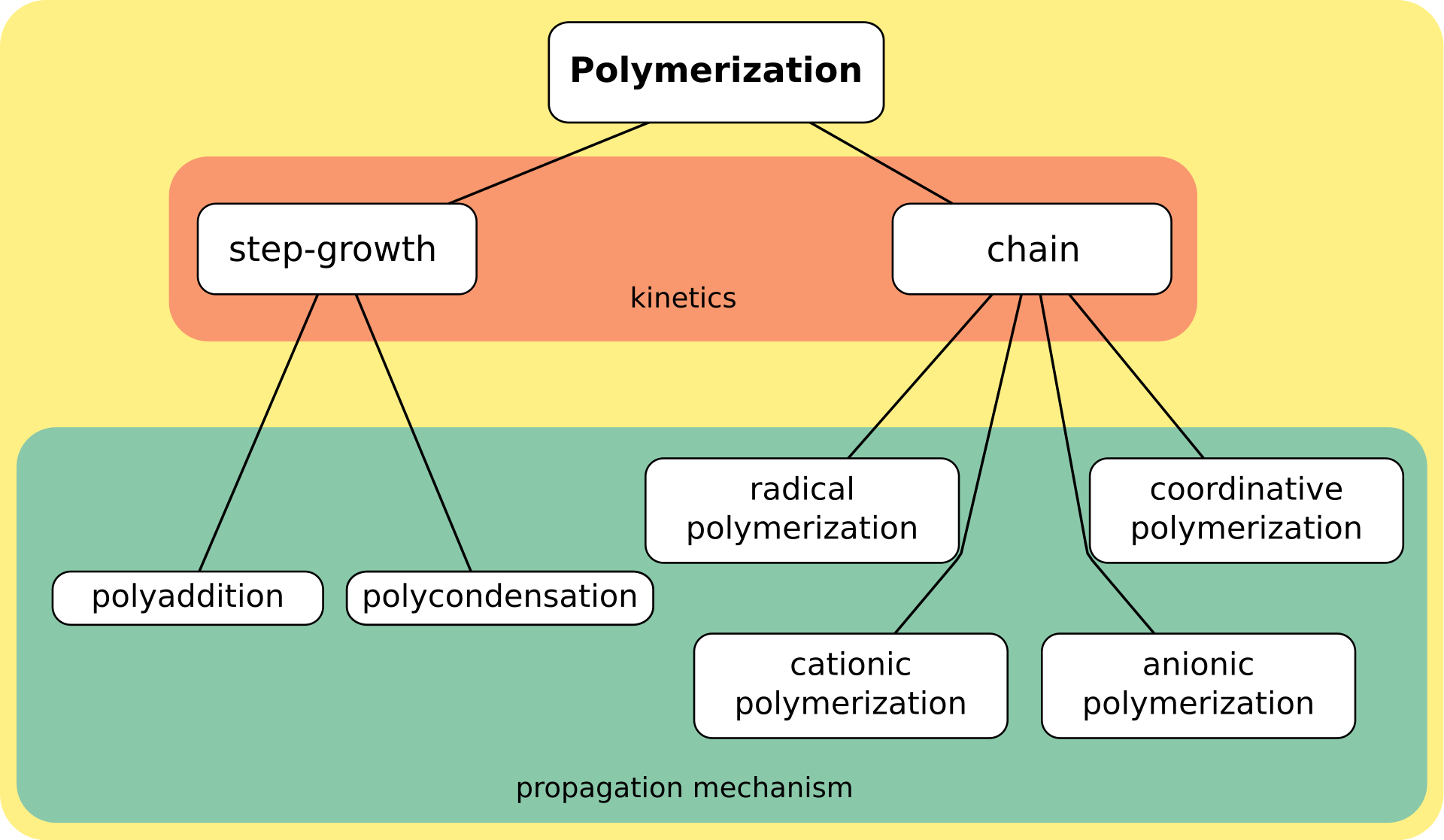
Synthetic methods are generally divided into two categories, step-growth polymerization
Step-growth polymerization refers to a type of polymerization mechanism in which bi-functional or multifunctional monomers react to form first dimers, then trimers, longer oligomers and eventually long chain polymers. Many naturally occurring a ...
and chain polymerization. The essential difference between the two is that in chain polymerization, monomers are added to the chain one at a time only, such as in polystyrene
Polystyrene (PS) is a synthetic polymer made from monomers of the aromatic hydrocarbon styrene. Polystyrene can be solid or foamed. General-purpose polystyrene is clear, hard, and brittle. It is an inexpensive resin per unit weight. It is a ...
, whereas in step-growth polymerization chains of monomers may combine with one another directly, such as in polyester
Polyester is a category of polymers that contain the ester functional group in every repeat unit of their main chain. As a specific material, it most commonly refers to a type called polyethylene terephthalate (PET). Polyesters include natural ...
. Step-growth polymerization can be divided into polycondensation
In polymer chemistry, condensation polymers are any kind of polymers whose process of polymerization involves a condensation reaction (i.e. a small molecule, such as water or methanol, is produced as a byproduct). Condensation polymers are for ...
, in which low-molar-mass by-product is formed in every reaction step, and polyaddition
Polyaddition (or addition polymerisation ) is a polymerization reaction that forms polymers via individual independent addition reactions. Polyaddition occurs as a reaction between functional groups on molecules with low degrees of polymerizat ...
.
 Newer methods, such as
Newer methods, such as plasma polymerization
Plasma polymerization (or glow discharge polymerization) uses plasma sources to generate a gas discharge that provides energy to activate or fragment gaseous or liquid monomer, often containing a vinyl group, in order to initiate polymerization. ...
do not fit neatly into either category. Synthetic polymerization reactions may be carried out with or without a catalyst
Catalysis () is the process of increasing the rate of a chemical reaction by adding a substance known as a catalyst (). Catalysts are not consumed in the reaction and remain unchanged after it. If the reaction is rapid and the catalyst recyc ...
. Laboratory synthesis of biopolymers, especially of proteins
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, respo ...
, is an area of intensive research.
Biological synthesis
 There are three main classes of biopolymers:
There are three main classes of biopolymers: polysaccharide
Polysaccharides (), or polycarbohydrates, are the most abundant carbohydrates found in food. They are long chain polymeric carbohydrates composed of monosaccharide units bound together by glycosidic linkages. This carbohydrate can react with wa ...
s, polypeptide
Peptides (, ) are short chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. Long chains of amino acids are called proteins. Chains of fewer than twenty amino acids are called oligopeptides, and include dipeptides, tripeptides, and tetrapeptides.
A p ...
s, and polynucleotide
A polynucleotide molecule is a biopolymer composed of 13 or more nucleotide monomers covalently bonded in a chain. DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) and RNA (ribonucleic acid) are examples of polynucleotides with distinct biological function. The pre ...
s.
In living cells, they may be synthesized by enzyme-mediated processes, such as the formation of DNA catalyzed by DNA polymerase
A DNA polymerase is a member of a family of enzymes that catalyze the synthesis of DNA molecules from nucleoside triphosphates, the molecular precursors of DNA. These enzymes are essential for DNA replication and usually work in groups to create ...
. The synthesis of proteins involves multiple enzyme-mediated processes to transcribe
Transcription refers to the process of converting sounds (voice, music etc.) into letters or musical notes, or producing a copy of something in another medium, including:
Genetics
* Transcription (biology), the copying of DNA into RNA, the fir ...
genetic information from the DNA to RNA
Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule essential in various biological roles in coding, decoding, regulation and expression of genes. RNA and deoxyribonucleic acid ( DNA) are nucleic acids. Along with lipids, proteins, and carbohydra ...
and subsequently translate
Translation is the communication of the meaning of a source-language text by means of an equivalent target-language text. The English language draws a terminological distinction (which does not exist in every language) between ''transl ...
that information to synthesize the specified protein from amino acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although hundreds of amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the alpha-amino acids, which comprise proteins. Only 22 alpha am ...
s. The protein may be modified further following translation in order to provide appropriate structure and functioning. There are other biopolymers such as rubber
Rubber, also called India rubber, latex, Amazonian rubber, ''caucho'', or ''caoutchouc'', as initially produced, consists of polymers of the organic compound isoprene, with minor impurities of other organic compounds. Thailand, Malaysia, and ...
, suberin
Suberin, cutin and lignins are complex, higher plant epidermis and periderm cell-wall macromolecules, forming a protective barrier. Suberin, a complex polyester biopolymer, is lipophilic, and composed of long chain fatty acids called suberin aci ...
, melanin
Melanin (; from el, μέλας, melas, black, dark) is a broad term for a group of natural pigments found in most organisms. Eumelanin is produced through a multistage chemical process known as melanogenesis, where the oxidation of the amino ...
, and lignin
Lignin is a class of complex organic polymers that form key structural materials in the support tissues of most plants. Lignins are particularly important in the formation of cell walls, especially in wood and bark, because they lend rigidity ...
.
Modification of natural polymers
Naturally occurring polymers such ascotton
Cotton is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll, or protective case, around the seeds of the cotton plants of the genus ''Gossypium'' in the mallow family Malvaceae. The fiber is almost pure cellulose, and can contain minor perce ...
, starch
Starch or amylum is a polymeric carbohydrate consisting of numerous glucose units joined by glycosidic bonds. This polysaccharide is produced by most green plants for energy storage. Worldwide, it is the most common carbohydrate in human diets ...
, and rubber were familiar materials for years before synthetic polymers such as polyethene
Polyethylene or polythene (abbreviated PE; IUPAC name polyethene or poly(methylene)) is the most commonly produced plastic. It is a polymer, primarily used for packaging (plastic bags, plastic films, geomembranes and containers including bott ...
and perspex
Poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA) belongs to a group of materials called engineering plastics. It is a transparent thermoplastic. PMMA is also known as acrylic, acrylic glass, as well as by the trade names and brands Crylux, Plexiglas, Acrylite ...
appeared on the market. Many commercially important polymers are synthesized by chemical modification of naturally occurring polymers. Prominent examples include the reaction of nitric acid
Nitric acid is the inorganic compound with the formula . It is a highly corrosive mineral acid. The compound is colorless, but older samples tend to be yellow cast due to decomposition into oxides of nitrogen. Most commercially available nitri ...
and cellulose
Cellulose is an organic compound with the formula , a polysaccharide consisting of a linear chain of several hundred to many thousands of β(1→4) linked D-glucose units. Cellulose is an important structural component of the primary cell wall ...
to form nitrocellulose
Nitrocellulose (also known as cellulose nitrate, flash paper, flash cotton, guncotton, pyroxylin and flash string, depending on form) is a highly flammable compound formed by nitrating cellulose through exposure to a mixture of nitric acid and ...
and the formation of vulcanized rubber
Vulcanization (British: Vulcanisation) is a range of processes for hardening rubbers. The term originally referred exclusively to the treatment of natural rubber with sulfur, which remains the most common practice. It has also grown to includ ...
by heating natural rubber in the presence of sulfur
Sulfur (or sulphur in British English) is a chemical element with the symbol S and atomic number 16. It is abundant, multivalent and nonmetallic. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules with a chemical formula ...
. Ways in which polymers can be modified include oxidation
Redox (reduction–oxidation, , ) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of substrate change. Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction is the gain of electrons or a d ...
, cross-link
In chemistry and biology a cross-link is a bond or a short sequence of bonds that links one polymer chain to another. These links may take the form of covalent bonds or ionic bonds and the polymers can be either synthetic polymers or natural ...
ing, and end-capping.
Structure
The structure of a polymeric material can be described at different length scales, from the sub-nm length scale up to the macroscopic one. There is in fact a hierarchy of structures, in which each stage provides the foundations for the next one. The starting point for the description of the structure of a polymer is the identity of its constituent monomers. Next, themicrostructure
Microstructure is the very small scale structure of a material, defined as the structure of a prepared surface of material as revealed by an optical microscope above 25× magnification. The microstructure of a material (such as metals, polymers ...
essentially describes the arrangement of these monomers within the polymer at the scale of a single chain. The microstructure determines the possibility for the polymer to form phases with different arrangements, for example through crystallization
Crystallization is the process by which solid forms, where the atoms or molecules are highly organized into a structure known as a crystal. Some ways by which crystals form are precipitating from a solution, freezing, or more rarely deposi ...
, the glass transition
The glass–liquid transition, or glass transition, is the gradual and reversible transition in amorphous materials (or in amorphous regions within semicrystalline materials) from a hard and relatively brittle "glassy" state into a viscous or rubb ...
or microphase separation.
These features play a major role in determining the physical and chemical properties of a polymer.
Monomers and repeat units
The identity of the repeat units (monomer residues, also known as "mers") comprising a polymer is its first and most important attribute. Polymer nomenclature is generally based upon the type of monomer residues comprising the polymer. A polymer which contains only a single type ofrepeat unit
In polymer chemistry, a repeat unit or repeating unit (or mer) is a part of a polymer whose repetition would produce the complete polymer chain (except for the end-groups) by linking the repeat units together successively along the chain, like the ...
is known as a homopolymer, while a polymer containing two or more types of repeat units is known as a copolymer
In polymer chemistry, a copolymer is a polymer derived from more than one species of monomer. The polymerization of monomers into copolymers is called copolymerization. Copolymers obtained from the copolymerization of two monomer species are some ...
. A terpolymer is a copolymer which contains three types of repeat units.
Polystyrene
Polystyrene (PS) is a synthetic polymer made from monomers of the aromatic hydrocarbon styrene. Polystyrene can be solid or foamed. General-purpose polystyrene is clear, hard, and brittle. It is an inexpensive resin per unit weight. It is a ...
is composed only of styrene
Styrene () is an organic compound with the chemical formula C6H5CH=CH2. This derivative of benzene is a colorless oily liquid, although aged samples can appear yellowish. The compound evaporates easily and has a sweet smell, although high concen ...
-based repeat units, and is classified as a homopolymer. Polyethylene terephthalate
Polyethylene terephthalate (or poly(ethylene terephthalate), PET, PETE, or the obsolete PETP or PET-P), is the most common thermoplastic polymer resin of the polyester family and is used in fibres for clothing, containers for liquids and foods ...
, even though produced from two different monomer
In chemistry, a monomer ( ; ''mono-'', "one" + '' -mer'', "part") is a molecule that can react together with other monomer molecules to form a larger polymer chain or three-dimensional network in a process called polymerization.
Classification
Mo ...
s (ethylene glycol
Ethylene glycol (IUPAC name: ethane-1,2-diol) is an organic compound (a vicinal diol) with the formula . It is mainly used for two purposes, as a raw material in the manufacture of polyester fibers and for antifreeze formulations. It is an odo ...
and terephthalic acid), is usually regarded as a homopolymer because only one type of repeat unit is formed. Ethylene-vinyl acetate contains more than one variety of repeat unit and is a copolymer. Some biological polymers are composed of a variety of different but structurally related monomer residues; for example, polynucleotide
A polynucleotide molecule is a biopolymer composed of 13 or more nucleotide monomers covalently bonded in a chain. DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) and RNA (ribonucleic acid) are examples of polynucleotides with distinct biological function. The pre ...
s such as DNA are composed of four types of nucleotide
Nucleotides are organic molecules consisting of a nucleoside and a phosphate. They serve as monomeric units of the nucleic acid polymers – deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA), both of which are essential biomolecules wi ...
subunits.
:
A polymer containing ionizable subunits (e.g., pendant carboxylic groups) is known as a polyelectrolyte
Polyelectrolytes are polymers whose repeating units bear an electrolyte group. Ion#Anions and cations, Polycations and polyanions are polyelectrolytes. These groups dissociation (chemistry), dissociate in aqueous solutions (water), making the pol ...
or ionomer
An ionomer () ('' iono-'' + ''-mer'') is a polymer composed of repeat units of both electrically neutral repeating units and ionized units covalently bonded to the polymer backbone as pendant group moieties. Usually no more than 15 mole percent ...
, when the fraction of ionizable units is large or small respectively.
Microstructure
The microstructure of a polymer (sometimes called configuration) relates to the physical arrangement of monomer residues along the backbone of the chain. These are the elements of polymer structure that require the breaking of a covalent bond in order to change. Various polymer structures can be produced depending on the monomers and reaction conditions: A polymer may consist of linear macromolecules containing each only one unbranched chain. In the case of unbranched polyethylene, this chain is a long-chain ''n''-alkane. There are also branched macromolecules with a main chain and side chains, in the case of polyethylene the side chains would bealkyl groups
In organic chemistry, an alkyl group is an alkane missing one hydrogen.
The term ''alkyl'' is intentionally unspecific to include many possible substitutions.
An acyclic alkyl has the general formula of . A cycloalkyl is derived from a cycloa ...
. In particular unbranched macromolecules can be in the solid state semi-crystalline, crystalline chain sections highlighted red in the figure below.
While branched and unbranched polymers are usually thermoplastics, many elastomer
An elastomer is a polymer with viscoelasticity (i.e. both viscosity and elasticity) and with weak intermolecular forces, generally low Young's modulus and high failure strain compared with other materials. The term, a portmanteau of ''elastic p ...
s have a wide-meshed cross-linking between the "main chains". Close-meshed crosslinking, on the other hand, leads to thermosets
In materials science, a thermosetting polymer, often called a thermoset, is a polymer that is obtained by irreversibly hardening (" curing") a soft solid or viscous liquid prepolymer (resin). Curing is induced by heat or suitable radiation and ...
. Cross-links and branches are shown as red dots in the figures. Highly branched polymers are amorphous and the molecules in the solid interact randomly.
:
Polymer architecture
comb polymers
In polymer chemistry, graft polymers are segmented copolymers with a linear backbone of one composite and randomly distributed branches of another composite. The picture labeled "graft polymer" shows how grafted chains of species B are covalent ...
, polymer brush
A polymer brush is the name given to a surface coating consisting of polymers tethered to a surface. The brush may be either in a solvated state, where the tethered polymer layer consists of polymer and solvent, or in a melt state, where the teth ...
es, dendronized polymer Dendronized polymers (or dendronised polymers) are linear polymers to every repeat unit of which dendrons are attached. Dendrons are regularly branched, tree-like fragments and for larger ones the polymer backbone is wrapped to give sausage-like, cy ...
s, ladder polymer
In chemistry, a ladder polymer is a type of double stranded polymer with the connectivity of a ladder. In a typical one-dimensional polymer, e.g. polyethylene and polysiloxanes, the monomers form two bonds, giving a chain. In a ladder polymer the ...
s, and dendrimer
Dendrimers are highly ordered, branched polymeric molecules. Synonymous terms for dendrimer include arborols and cascade molecules. Typically, dendrimers are symmetric about the core, and often adopt a spherical three-dimensional morphology. The ...
s. There exist also two-dimensional polymers (2DP) which are composed of topologically planar repeat units. A polymer's architecture affects many of its physical properties including solution viscosity, melt viscosity, solubility in various solvents, glass-transition temperature and the size of individual polymer coils in solution. A variety of techniques may be employed for the synthesis of a polymeric material with a range of architectures, for example living polymerization
In polymer chemistry, living polymerization is a form of chain growth polymerization where the ability of a growing polymer chain to terminate has been removed. This can be accomplished in a variety of ways. Chain termination and chain transfer ...
.
Chain length
A common means of expressing the length of a chain is thedegree of polymerization
The degree of polymerization, or DP, is the number of monomeric units in a macromolecule or polymer or oligomer molecule.
For a homopolymer, there is only one type of monomeric unit and the ''number-average'' degree of polymerization is given b ...
, which quantifies the number of monomers incorporated into the chain.Rubinstein, p. 3 As with other molecules, a polymer's size may also be expressed in terms of molecular weight
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms held together by attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions which satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemistry, and bioch ...
. Since synthetic polymerization techniques typically yield a statistical distribution of chain lengths, the molecular weight is expressed in terms of weighted averages. The number-average molecular weight The molar mass distribution (or molecular weight distribution) describes the relationship between the number of Mole (unit), moles of each polymer species (Ni) and the molar mass (Mi) of that species. In linear polymers, the individual polymer chain ...
(''M''n) and weight-average molecular weight (''M''w) are most commonly reported.Rubinstein, pp. 23–24 The ratio of these two values (''M''w / ''M''n) is the dispersity
In chemistry, the dispersity is a measure of the heterogeneity of sizes of molecules or particles in a mixture. A collection of objects is called uniform if the objects have the same size, shape, or mass. A sample of objects that have an inconsi ...
(''Đ''), which is commonly used to express the width of the molecular weight distribution.
The physical properties of polymer strongly depend on the length (or equivalently, the molecular weight) of the polymer chain.Rubinstein, p. 5 One important example of the physical consequences of the molecular weight is the scaling of the viscosity
The viscosity of a fluid is a measure of its resistance to deformation at a given rate. For liquids, it corresponds to the informal concept of "thickness": for example, syrup has a higher viscosity than water.
Viscosity quantifies the inte ...
(resistance to flow) in the melt. The influence of the weight-average molecular weight () on the melt viscosity () depends on whether the polymer is above or below the onset of entanglements
''Entanglements'' is the third full-length album from indie rock ensemble Parenthetical Girls.
Track listing
#"Four Words" - 3:10
#"Avenue of Trees" - 3:17
#"Unmentionables" - 1:51
#"Gut Symmetries" - 3:58
#"A Song for Ellie Greenwich
Ele ...
. Below the entanglement molecular weight, , whereas above the entanglement molecular weight, . In the latter case, increasing the polymer chain length 10-fold would increase the viscosity over 1000 times. Increasing chain length furthermore tends to decrease chain mobility, increase strength and toughness, and increase the glass-transition temperature (Tg). This is a result of the increase in chain interactions such as van der Waals attractions and entanglements
''Entanglements'' is the third full-length album from indie rock ensemble Parenthetical Girls.
Track listing
#"Four Words" - 3:10
#"Avenue of Trees" - 3:17
#"Unmentionables" - 1:51
#"Gut Symmetries" - 3:58
#"A Song for Ellie Greenwich
Ele ...
that come with increased chain length. These interactions tend to fix the individual chains more strongly in position and resist deformations and matrix breakup, both at higher stresses and higher temperatures.
Monomer arrangement in copolymers
Copolymers are classified either as statistical copolymers, alternating copolymers, block copolymers, graft copolymers or gradient copolymers. In the schematic figure below, Ⓐ and Ⓑ symbolize the tworepeat unit
In polymer chemistry, a repeat unit or repeating unit (or mer) is a part of a polymer whose repetition would produce the complete polymer chain (except for the end-groups) by linking the repeat units together successively along the chain, like the ...
s.
:
*Alternating copolymers possess two regularly alternating monomer residues:Painter, p. 14 . An example is the equimolar copolymer of styrene
Styrene () is an organic compound with the chemical formula C6H5CH=CH2. This derivative of benzene is a colorless oily liquid, although aged samples can appear yellowish. The compound evaporates easily and has a sweet smell, although high concen ...
and maleic anhydride
Maleic anhydride is an organic compound with the formula C2H2(CO)2O. It is the acid anhydride of maleic acid. It is a colorless or white solid with an acrid odor. It is produced industrially on a large scale for applications in coatings and pol ...
formed by free-radical chain-growth polymerization.Rudin p.18-20 A step-growth copolymer such as Nylon 66
Nylon 66 (loosely written nylon 6-6, nylon 6/6, nylon 6,6, or nylon 6:6) is a type of polyamide or nylon. It, and nylon 6, are the two most common for textile and plastic industries. Nylon 66 is made of two monomers each containing 6 carbon atoms, ...
can also be considered a strictly alternating copolymer of diamine and diacid residues, but is often described as a homopolymer with the dimeric residue of one amine and one acid as a repeat unit.Cowie p.104
*Periodic copolymers have more than two species of monomer units in a regular sequence.
*Statistical copolymers have monomer residues arranged according to a statistical rule. A statistical copolymer in which the probability of finding a particular type of monomer residue at a particular point in the chain is independent of the types of surrounding monomer residue may be referred to as a truly random copolymer.Painter, p. 15 For example, the chain-growth copolymer of vinyl chloride
Vinyl chloride is an organochloride with the formula H2C=CHCl. It is also called vinyl chloride monomer (VCM) or chloroethene. This colorless compound is an important industrial chemical chiefly used to produce the polymer polyvinyl chloride (PVC ...
and vinyl acetate
Vinyl acetate is an organic compound with the formula CH3CO2CH=CH2. This colorless liquid is the precursor to polyvinyl acetate and ethene-vinyl acetate copolymers, important industrial polymers.
Production
The worldwide production capacity of v ...
is random.
*Block copolymers have long sequences of different monomer units. Polymers with two or three blocks of two distinct chemical species (e.g., A and B) are called diblock copolymers and triblock copolymers, respectively. Polymers with three blocks, each of a different chemical species (e.g., A, B, and C) are termed triblock terpolymers.
*Graft or grafted copolymers contain side chains or branches whose repeat units have a different composition or configuration than the main chain. The branches are added on to a preformed main chain macromolecule.
Monomers within a copolymer may be organized along the backbone in a variety of ways. A copolymer containing a controlled arrangement of monomers is called a sequence-controlled polymer
A sequence-controlled polymer is a macromolecule, in which the sequence of monomers is controlled to some degree. This control can be absolute but not necessarily. In other words, a sequence-controlled polymer can be uniform (its dispersity Ð is ...
. Alternating, periodic and block copolymers are simple examples of sequence-controlled polymer
A sequence-controlled polymer is a macromolecule, in which the sequence of monomers is controlled to some degree. This control can be absolute but not necessarily. In other words, a sequence-controlled polymer can be uniform (its dispersity Ð is ...
s.
Tacticity
Tacticity describes the relativestereochemistry
Stereochemistry, a subdiscipline of chemistry, involves the study of the relative spatial arrangement of atoms that form the structure of molecules and their manipulation. The study of stereochemistry focuses on the relationships between stereois ...
of chiral
Chirality is a property of asymmetry important in several branches of science. The word ''chirality'' is derived from the Greek (''kheir''), "hand", a familiar chiral object.
An object or a system is ''chiral'' if it is distinguishable from ...
centers in neighboring structural units within a macromolecule. There are three types of tacticity: isotactic
Tacticity (from el, τακτικός, taktikos, "relating to arrangement or order") is the relative stereochemistry of adjacent chiral centers within a macromolecule. The practical significance of tacticity rests on the effects on the physical p ...
(all substituents on the same side), atactic
Tacticity (from el, τακτικός, taktikos, "relating to arrangement or order") is the relative stereochemistry of adjacent chiral centers within a macromolecule. The practical significance of tacticity rests on the effects on the physical p ...
(random placement of substituents), and syndiotactic
Tacticity (from el, τακτικός, taktikos, "relating to arrangement or order") is the relative stereochemistry of adjacent chiral centers within a macromolecule. The practical significance of tacticity rests on the effects on the physical p ...
(alternating placement of substituents).
:
Morphology
Polymer morphology generally describes the arrangement and microscale ordering of polymer chains in space. The macroscopic physical properties of a polymer are related to the interactions between the polymer chains. * Disordered polymers: In the solid state, atactic polymers, polymers with a high degree of branching and random copolymers formamorphous
In condensed matter physics and materials science, an amorphous solid (or non-crystalline solid, glassy solid) is a solid that lacks the long-range order that is characteristic of a crystal.
Etymology
The term comes from the Greek ''a'' ("wi ...
(i.e. glassy structures).Bernd Tieke: ''Makromolekulare Chemie.'' 3. Auflage, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim 2014, S. 295f (in German). In melt and solution, polymers tend to form a constantly changing "statistical cluster", see freely-jointed-chain model. In the solid state, the respective conformations of the molecules are frozen. Hooking and entanglement of chain molecules lead to a "mechanical bond" between the chains. Intermolecular
An intermolecular force (IMF) (or secondary force) is the force that mediates interaction between molecules, including the electromagnetic forces of attraction
or repulsion which act between atoms and other types of neighbouring particles, e.g. a ...
and intramolecular attractive forces only occur at sites where molecule segments are close enough to each other. The irregular structures of the molecules prevent a narrower arrangement.
* Linear polymers with periodic structure, low branching and stereoregularity (e. g. not atactic) have a semi-crystalline
Crystallinity refers to the degree of structural order in a solid. In a crystal, the atoms or molecules are arranged in a regular, periodic manner. The degree of crystallinity has a big influence on hardness, density, transparency and diffusion ...
structure in the solid state. In simple polymers (such as polyethylene), the chains are present in the crystal in zigzag conformation. Several zigzag conformations form dense chain packs, called crystallites or lamellae. The lamellae are much thinner than the polymers are long (often about 10 nm). Wolfgang Kaiser: ''Kunststoffchemie für Ingenieure.'' 3. Auflage, Carl Hanser, München 2011, S. 84. They are formed by more or less regular folding of one or more molecular chains. Amorphous structures exist between the lamellae. Individual molecules can lead to entanglements between the lamellae and can also be involved in the formation of two (or more) lamellae (chains than called tie molecules). Several lamellae form a superstructure, a spherulite
In petrology, spherulites () are small, rounded bodies that commonly occur in volcanic glass, vitreous igneous rocks. They are often visible in specimens of obsidian, pitchstone, and rhyolite as globules about the size of millet seed or rice g ...
, often with a diameter in the range of 0.05 to 1 mm.
:The type and arrangement of (functional) residues of the repeat units effects or determines the crystallinity and strength of the secondary valence bonds. In isotactic polypropylene, the molecules form a helix. Like the zigzag conformation, such helices allow a dense chain packing. Particularly strong intermolecular interactions occur when the residues of the repeating units allow the formation of hydrogen bond
In chemistry, a hydrogen bond (or H-bond) is a primarily electrostatic force of attraction between a hydrogen (H) atom which is covalently bound to a more electronegative "donor" atom or group (Dn), and another electronegative atom bearing a ...
s, as in the case of ''p''-aramid. The formation of strong intramolecular associations may produce diverse folded states of single linear chains with distinct circuit topology
The circuit topology of a folded linear polymer refers to the arrangement of its intra-molecular contacts. Examples of linear polymers with intra-molecular contacts are nucleic acids and proteins. Proteins fold via formation of contacts of variou ...
. Crystallinity and superstructure are always dependent on the conditions of their formation, see also: crystallization of polymers
Crystallization of polymers is a process associated with partial alignment of their molecular chains. These chains fold together and form ordered regions called Lamella (materials), lamellae, which compose larger spheroidal structures named Spheru ...
. Compared to amorphous structures, semi-crystalline structures lead to a higher stiffness, density, melting temperature and higher resistance of a polymer.
* Cross-linked polymers: Wide-meshed cross-linked polymers are elastomer
An elastomer is a polymer with viscoelasticity (i.e. both viscosity and elasticity) and with weak intermolecular forces, generally low Young's modulus and high failure strain compared with other materials. The term, a portmanteau of ''elastic p ...
s and cannot be molten (unlike thermoplastic
A thermoplastic, or thermosoft plastic, is any plastic polymer material that becomes pliable or moldable at a certain elevated temperature and solidifies upon cooling.
Most thermoplastics have a high molecular weight. The polymer chains associate ...
s); heating cross-linked polymers only leads to decomposition
Decomposition or rot is the process by which dead organic substances are broken down into simpler organic or inorganic matter such as carbon dioxide, water, simple sugars and mineral salts. The process is a part of the nutrient cycle and is e ...
. Thermoplastic elastomers, on the other hand, are reversibly "physically crosslinked" and can be molten. Block copolymers in which a hard segment of the polymer has a tendency to crystallize and a soft segment has an amorphous structure are one type of thermoplastic elastomers: the hard segments ensure wide-meshed, physical crosslinking.
Crystallinity
When applied to polymers, the term ''crystalline'' has a somewhat ambiguous usage. In some cases, the term ''crystalline'' finds identical usage to that used in conventional crystallography. For example, the structure of a crystalline protein or polynucleotide, such as a sample prepared for x-ray crystallography, may be defined in terms of a conventional unit cell composed of one or more polymer molecules with cell dimensions of hundreds of angstroms or more. A synthetic polymer may be loosely described as crystalline if it contains regions of three-dimensional ordering on atomic (rather than macromolecular) length scales, usually arising from intramolecular folding or stacking of adjacent chains. Synthetic polymers may consist of both crystalline and amorphous regions; the degree of crystallinity may be expressed in terms of a weight fraction or volume fraction of crystalline material. Few synthetic polymers are entirely crystalline. The crystallinity of polymers is characterized by their degree of crystallinity, ranging from zero for a completely non-crystalline polymer to one for a theoretical completely crystalline polymer. Polymers with microcrystalline regions are generally tougher (can be bent more without breaking) and more impact-resistant than totally amorphous polymers. Polymers with a degree of crystallinity approaching zero or one will tend to be transparent, while polymers with intermediate degrees of crystallinity will tend to be opaque due to light scattering by crystalline or glassy regions. For many polymers, crystallinity may also be associated with decreased transparency.Chain conformation
The space occupied by a polymer molecule is generally expressed in terms of radius of gyration, which is an average distance from the center of mass of the chain to the chain itself. Alternatively, it may be expressed in terms of pervaded volume, which is the volume spanned by the polymer chain and scales with the cube of the radius of gyration. The simplest theoretical models for polymers in the molten, amorphous state are ideal chains.Properties
Polymer properties depend of their structure and they are divided into classes according to their physical bases. Many physical and chemical properties describe how a polymer behaves as a continuous macroscopic material. They are classified as bulk properties, or Intensive and extensive properties#Intensive properties, intensive properties according to thermodynamics.Mechanical properties
 The bulk properties of a polymer are those most often of end-use interest. These are the properties that dictate how the polymer actually behaves on a macroscopic scale.
The bulk properties of a polymer are those most often of end-use interest. These are the properties that dictate how the polymer actually behaves on a macroscopic scale.
Tensile strength
The tensile strength of a material quantifies how much elongating stress the material will endure before failure. This is very important in applications that rely upon a polymer's physical strength or durability. For example, a rubber band with a higher tensile strength will hold a greater weight before snapping. In general, tensile strength increases with polymer chain length and cross-link, crosslinking of polymer chains.Young's modulus of elasticity
Young's modulus quantifies the elasticity (physics), elasticity of the polymer. It is defined, for small deformation (mechanics)#Strain, strains, as the ratio of rate of change of stress to strain. Like tensile strength, this is highly relevant in polymer applications involving the physical properties of polymers, such as rubber bands. The modulus is strongly dependent on temperature. Viscoelasticity describes a complex time-dependent elastic response, which will exhibit hysteresis in the stress-strain curve when the load is removed. Dynamic mechanical analysis or DMA measures this complex modulus by oscillating the load and measuring the resulting strain as a function of time.Transport properties
Transport phenomena, Transport properties such as mass diffusivity, diffusivity describe how rapidly molecules move through the polymer matrix. These are very important in many applications of polymers for films and membranes. The movement of individual macromolecules occurs by a process called reptation in which each chain molecule is constrained by entanglements with neighboring chains to move within a virtual tube. The theory of reptation can explain polymer molecule dynamics andviscoelasticity
In materials science and continuum mechanics, viscoelasticity is the property of materials that exhibit both viscous and elastic characteristics when undergoing deformation. Viscous materials, like water, resist shear flow and strain linearly wi ...
.
Phase behavior
Crystallization and melting
Depending on their chemical structures, polymers may be either semi-crystalline or amorphous. Semi-crystalline polymers can undergo crystallization of polymers, crystallization and melting transitions, whereas amorphous polymers do not. In polymers, crystallization and melting do not suggest solid-liquid phase transitions, as in the case of water or other molecular fluids. Instead, crystallization and melting refer to the phase transitions between two solid states (''i.e.'', semi-crystalline and amorphous). Crystallization occurs above the glass-transition temperature (''T''g) and below the melting temperature (''T''m).Glass transition
All polymers (amorphous or semi-crystalline) go throughglass transition
The glass–liquid transition, or glass transition, is the gradual and reversible transition in amorphous materials (or in amorphous regions within semicrystalline materials) from a hard and relatively brittle "glassy" state into a viscous or rubb ...
s. The glass-transition temperature (''T''g) is a crucial physical parameter for polymer manufacturing, processing, and use. Below ''T''g, molecular motions are frozen and polymers are brittle and glassy. Above ''T''g, molecular motions are activated and polymers are rubbery and viscous. The glass-transition temperature may be engineered by altering the degree of branching or crosslinking in the polymer or by the addition of plasticizers.
Whereas crystallization and melting are first-order phase transitions, the glass transition is not. The glass transition shares features of second-order phase transitions (such as discontinuity in the heat capacity, as shown in the figure), but it is generally not considered a thermodynamic transition between equilibrium states.
Mixing behavior
small molecule
Within the fields of molecular biology and pharmacology, a small molecule or micromolecule is a low molecular weight (≤ 1000 daltons) organic compound that may regulate a biological process, with a size on the order of 1 nm. Many drugs ar ...
materials. This effect results from the fact that the driving force for mixing is usually entropy, not interaction energy. In other words, miscible materials usually form a solution not because their interaction with each other is more favorable than their self-interaction, but because of an increase in entropy and hence free energy associated with increasing the amount of volume available to each component. This increase in entropy scales with the number of particles (or moles) being mixed. Since polymeric molecules are much larger and hence generally have much higher specific volumes than small molecules, the number of molecules involved in a polymeric mixture is far smaller than the number in a small molecule mixture of equal volume. The energetics of mixing, on the other hand, is comparable on a per volume basis for polymeric and small molecule mixtures. This tends to increase the free energy of mixing for polymer solutions and thereby making solvation less favorable, and thereby making the availability of concentrated solutions of polymers far rarer than those of small molecules.
Furthermore, the phase behavior of polymer solutions and mixtures is more complex than that of small molecule mixtures. Whereas most small molecule solutions exhibit only an upper critical solution temperature phase transition (UCST), at which phase separation occurs with cooling, polymer mixtures commonly exhibit a lower critical solution temperature phase transition (LCST), at which phase separation occurs with heating.
In dilute solutions, the properties of the polymer are characterized by the interaction between the solvent and the polymer. In a good solvent, the polymer appears swollen and occupies a large volume. In this scenario, intermolecular forces between the solvent and monomer subunits dominate over intramolecular interactions. In a bad solvent or poor solvent, intramolecular forces dominate and the chain contracts. In the theta solvent, or the state of the polymer solution where the value of the second virial coefficient becomes 0, the intermolecular polymer-solvent repulsion balances exactly the intramolecular monomer-monomer attraction. Under the theta condition (also called the Paul J. Flory, Flory condition), the polymer behaves like an ideal random coil. The transition between the states is known as a coil–globule transition.
Inclusion of plasticizers
Inclusion of plasticizers tends to lower Tg and increase polymer flexibility. Addition of the plasticizer will also modify dependence of the glass-transition temperature Tg on the cooling rate. The mobility of the chain can further change if the molecules of plasticizer give rise to hydrogen bonding formation. Plasticizers are generally small molecules that are chemically similar to the polymer and create gaps between polymer chains for greater mobility and fewer interchain interactions. A good example of the action of plasticizers is related to polyvinylchlorides or PVCs. A uPVC, or unplasticized polyvinylchloride, is used for things such as pipes. A pipe has no plasticizers in it, because it needs to remain strong and heat-resistant. Plasticized PVC is used in clothing for a flexible quality. Plasticizers are also put in some types of cling film to make the polymer more flexible.Chemical properties
The attractive forces between polymer chains play a large part in determining the polymer’s properties. Because polymer chains are so long, they have many such interchain interactions per molecule, amplifying the effect of these interactions on the polymer properties in comparison to attractions between conventional molecules. Different side groups on the polymer can lend the polymer to ionic bonding or hydrogen bonding between its own chains. These stronger forces typically result in higher tensile strength and higher crystalline melting points. The intermolecular forces in polymers can be affected by dipoles in the monomer units. Polymers containing amide or carbonyl groups can formhydrogen bond
In chemistry, a hydrogen bond (or H-bond) is a primarily electrostatic force of attraction between a hydrogen (H) atom which is covalently bound to a more electronegative "donor" atom or group (Dn), and another electronegative atom bearing a ...
s between adjacent chains; the partially positively charged hydrogen atoms in N-H groups of one chain are strongly attracted to the partially negatively charged oxygen atoms in C=O groups on another. These strong hydrogen bonds, for example, result in the high tensile strength and melting point of polymers containing carbamate, urethane or urea linkages. Polyesters have intermolecular force#Dipole-dipole interactions, dipole-dipole bonding between the oxygen atoms in C=O groups and the hydrogen atoms in H-C groups. Dipole bonding is not as strong as hydrogen bonding, so a polyester's melting point and strength are lower than Kevlar's (Twaron), but polyesters have greater flexibility. Polymers with non-polar units such as polyethylene interact only through weak Van der Waals forces. As a result, they typically have lower melting temperatures than other polymers.
When a polymer is dispersed or dissolved in a liquid, such as in commercial products like paints and glues, the chemical properties and molecular interactions influence how the solution flows and can even lead to self-assembly of the polymer into complex structures. When a polymer is applied as a coating, the chemical properties will influence the adhesion of the coating and how it interacts with external materials, such as superhydrophobic polymer coatings leading to water resistance. Overall the chemical properties of a polymer are important elements for designing new polymeric material products.
Optical properties
Polymers such as poly(methyl methacrylate), PMMA and HEMA:MMA are used as matrices in the gain medium of solid-state dye lasers, also known as solid-state dye-doped polymer lasers. These polymers have a high surface quality and are also highly transparent so that the laser properties are dominated by the laser dye used to dope the polymer matrix. These type of lasers, that also belong to the class of organic lasers, are known to yield very narrow laser linewidth, linewidths which is useful for spectroscopy and analytical applications. An important optical parameter in the polymer used in laser applications is the change in refractive index with temperature also known as dn/dT. For the polymers mentioned here the (dn/dT) ~ −1.4 × 10−4 in units of K−1 in the 297 ≤ T ≤ 337 K range.Electrical properties
Most conventional polymers such as polyethylene are Insulator (electricity), electrical insulators, but the development of polymers containing Conjugated system, π-conjugated bonds has led to a wealth of polymer-based semiconductors, such as polythiophenes. This has led to many applications in the field of organic electronics.Applications
Nowadays, synthetic polymers are used in almost all walks of life. Modern society would look very different without them. The spreading of polymer use is connected to their unique properties: low density, low cost, good thermal/electrical insulation properties, high resistance to corrosion, low-energy demanding polymer manufacture and facile processing into final products. For a given application, the properties of a polymer can be tuned or enhanced by combination with other materials, as in Polymer matrix composite, composites. Their application allows to save energy (lighter cars and planes, thermally insulated buildings), protect food and drinking water (packaging), save land and lower use of fertilizers (synthetic fibres), preserve other materials (coatings), protect and save lifes (hygiene, medical applications). A representative, non-exhaustive list of applications is given below. * Clothing, sportswear and accessories: Polyester#Uses and applications, polyester and PVC clothing, spandex, sneakers, sport shoes, wetsuits, Ball (association football), footballs and Billiard ball#Snooker, billiard balls, skis and snowboards, Racket (sports equipment), rackets, parachutes, sailcloth, sails, tent, tents and shelters. * Electronic and photonic technologies: organic Organic electronics, field effect transistors (OFET), OLED#Polymer light-emitting diodes, light emitting diodes (OLED) and organic solar cell, solar cells, Television set, television components, compact discs (CD), photoresists, holography. * Packaging and containers: Plastic film, films, Plastic bottle, bottles, food packaging, barrels. * Insulation: Insulator (electricity), electrical and thermal insulation, spray foams. * Construction and structural applications: garden furniture, polyvinyl chloride, PVC windows, flooring, seal (mechanical), sealing, Plastic pipework, pipes. * Paints, glues and lubricants: varnish, adhesives, dispersants, anti-graffiti coatings, Biofouling#Non-toxic coatings, antifouling coatings, non-stick surfaces, lubricants. * Car parts: tires, Bumper (car), bumpers, windshields, windscreen wipers, fuel tanks, car seats. * Household items: buckets, kitchenware, toys (e.g., construction sets and Rubik's cube). * Medical applications: Blood transfusion, blood bag, syringes, rubber gloves, surgical suture, contact lenses, prosthesis, Drug carrier, controlled drug delivery and release, Growth medium, matrices for cell growth. * Personal hygiene and healthcare: diapers using superabsorbent polymers, toothbrushes, cosmetics, shampoo, condoms. * Security: personal protective equipment, bulletproof vests, space suits, ropes. * Separation technologies: synthetic membranes, Fuel cell#Proton-exchange membrane fuel cells (PEMFCs), fuel cell membranes, filtration, ion-exchange resins. * Money: polymer banknotes and payment cards. * 3D printing.Standardized nomenclature
There are multiple conventions for naming polymer substances. Many commonly used polymers, such as those found in consumer products, are referred to by a common or trivial name. The trivial name is assigned based on historical precedent or popular usage rather than a standardized naming convention. Both the American Chemical Society (ACS) andIUPAC
The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC ) is an international federation of National Adhering Organizations working for the advancement of the chemical sciences, especially by developing nomenclature and terminology. It is ...
have proposed standardized naming conventions; the ACS and IUPAC conventions are similar but not identical. Examples of the differences between the various naming conventions are given in the table below:
In both standardized conventions, the polymers' names are intended to reflect the monomer(s) from which they are synthesized (source based nomenclature) rather than the precise nature of the repeating subunit. For example, the polymer synthesized from the simple alkene ethene is called polyethene, retaining the ''-ene'' suffix even though the double bond is removed during the polymerization process:
:→
:However, IUPAC structure based nomenclature is based on naming of the preferred Repeat unit, constitutional repeating unit.
Characterization
Polymer characterization spans many techniques for determining the chemical composition, molecular weight distribution, and physical properties. Select common techniques include the following: *Size-exclusion chromatography (also called gel permeation chromatography), sometimes coupled with static light scattering, can used to determine the number-average molecular weight, weight-average molecular weight, and polydispersity, dispersity. *Scattering techniques, such as static light scattering and small-angle neutron scattering, are used to determine the dimensions (radius of gyration) of macromolecules in solution or in the melt. These techniques are also used to characterize the three-dimensional structure of microphase-separated block polymers, polymeric micelles, and other materials. *Wide-angle X-ray scattering (also called wide-angle X-ray diffraction) is used to determine the crystalline structure of polymers (or lack thereof). *Spectroscopy techniques, including FTIR, Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy, Raman spectroscopy, and nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, can be used to determine the chemical composition. *Differential scanning calorimetry is used to characterize the thermal properties of polymers, such as the glass-transition temperature, crystallization temperature, and melting temperature. The glass-transition temperature can also be determined by dynamic mechanical analysis. *Thermogravimetry is a useful technique to evaluate the thermal stability of the polymer. *Rheology is used to characterize the flow and deformation behavior. It can be used to determine theviscosity
The viscosity of a fluid is a measure of its resistance to deformation at a given rate. For liquids, it corresponds to the informal concept of "thickness": for example, syrup has a higher viscosity than water.
Viscosity quantifies the inte ...
, elastic modulus, modulus, and other rheological properties. Rheology is also often used to determine the molecular architecture (molecular weight, molecular weight distribution, branching) and to understand how the polymer can be processed.
Degradation
Polymer degradation is a change in the properties—tensile strength, color, shape, or molecular weight—of a polymer or polymer-based product under the influence of one or more environmental factors, such as heat, light, and the presence of certain chemicals, oxygen, and enzymes. This change in properties is often the result of bond breaking in the polymer backbone (chain scission) which may occur at the chain ends or at random positions in the chain. Although such changes are frequently undesirable, in some cases, such as biodegradation and recycling, they may be intended to prevent environmental pollution. Degradation can also be useful in biomedical settings. For example, a copolymer of polylactic acid and polyglycolic acid is employed in hydrolysable stitches that slowly degrade after they are applied to a wound. The susceptibility of a polymer to degradation depends on its structure. Epoxies and chains containing aromatic functionalities are especially susceptible to UV degradation while polyesters are susceptible to degradation by hydrolysis. Polymers containing an Saturated and unsaturated compounds, unsaturated backbone degrade via ozone cracking. Carbon based polymers are more susceptible to thermal degradation than inorganic polymers such as polydimethylsiloxane and are therefore not ideal for most high-temperature applications. The degradation of polyethylene occurs by random scission—a random breakage of the bonds that hold the atoms of the polymer together. When heated above 450 °C, polyethylene degrades to form a mixture of hydrocarbons. In the case of chain-end scission, monomers are released and this process is referred to as unzipping or depolymerization. Which mechanism dominates will depend on the type of polymer and temperature; in general, polymers with no or a single small substituent in the repeat unit will decompose via random-chain scission. The sorting of polymer waste for recycling purposes may be facilitated by the use of the resin identification codes developed by the Society of the Plastics Industry to identify the type of plastic.Product failure
Failure of safety-critical polymer components can cause serious accidents, such as fire in the case of cracked and degraded polymer fuel lines. Chlorine-induced cracking of acetal resin plumbing joints and polybutylene pipes has caused many serious floods in domestic properties, especially in the US in the 1990s. Traces of chlorine in the water supply attacked polymers present in the plumbing, a problem which occurs faster if any of the parts have been poorly extruded or Injection molding, injection molded. Attack of the acetal joint occurred because of faulty molding, leading to cracking along the threads of the fitting where there is stress concentration. Polymer oxidation has caused accidents involving medical devices. One of the oldest known failure modes is ozone cracking caused by chain scission when ozone gas attacks susceptibleelastomer
An elastomer is a polymer with viscoelasticity (i.e. both viscosity and elasticity) and with weak intermolecular forces, generally low Young's modulus and high failure strain compared with other materials. The term, a portmanteau of ''elastic p ...
s, such as natural rubber
Rubber, also called India rubber, latex, Amazonian rubber, ''caucho'', or ''caoutchouc'', as initially produced, consists of polymers of the organic compound isoprene, with minor impurities of other organic compounds. Thailand, Malaysia, and ...
and nitrile rubber. They possess double bonds in their repeat units which are cleaved during ozonolysis. Cracks in fuel lines can penetrate the bore of the tube and cause fuel leakage. If cracking occurs in the engine compartment, electric sparks can ignite the gasoline and can cause a serious fire. In medical use degradation of polymers can lead to changes of physical and chemical characteristics of implantable devices.
Nylon 6,6, Nylon 66 is susceptible to acid hydrolysis, and in one accident, a fractured fuel line led to a spillage of diesel into the road. If diesel fuel leaks onto the road, accidents to following cars can be caused by the slippery nature of the deposit, which is like black ice. Furthermore, the asphalt concrete road surface will suffer damage as a result of the diesel fuel dissolving the asphaltenes from the composite material, this resulting in the degradation of the asphalt surface and structural integrity of the road.
See also
*Biopolymer *Ideal chain *Catenation *Inorganic polymer *List of important publications in chemistry#Polymer chemistry, Important publications in polymer chemistry *Oligomer *Polymer adsorption *Polymer classes (disambiguation), Polymer classes *Polymer engineering *Polymerization *Merosity, Polymery (botany) *Reactive compatibilization *Sequence-controlled polymer *Shape-memory polymer *Sol–gel process *Supramolecular polymer *Thermoplastic *Thermosetting polymerReferences
Bibliography
* * * *External links
How to Analyze Polymers Using X-ray Diffraction
{{Portal bar, Science, Chemistry, Numismatics, Electronics, Algae, Money Organic polymers, Polymers, Polymer chemistry Soft matter Materials science